High-performance LED headlight
The newly developed high-performance LED headlight also shows that Volkswagen is investigating all evolutionary paths of light. It is an inexpensive but powerful alternative to laser light. The laser light is primarily used for range-generating main beam applications. The same applies to the high-current LED main beam. It is intended to improve night-time safety by maximising the light intensity of the main beam. The high-performance LED headlight was developed in-house by Volkswagen. In addition, the optical light output in these main beam systems can be reduced to provide attractive, compact headlights without reducing the light output. The same is also possible for dipped beam headlight systems.
Even the best light must be affordable
Laser light is considered to be an ideal light source because a lot of light is emitted from an extremely small area. The result is a high level of luminance. This gives rise to an almost perfect point light source. In addition, the systems in the vehicle can become smaller due to the high intensity of the laser light. It thereby offers a very large range and at the same time great advantages for vehicle design. But for a volume manufacturer like Volkswagen, there is also a downside to laser light. Compared to normal LED headlights, the costs are significantly higher for various technical reasons, and even large quantities will only slowly decrease these costs. However, the top priority for Volkswagen is the principle that safety must be affordable. For this reason, Volkswagen's lighting engineers have pushed the development of the high-performance LED headlight as an alternative to laser light as a new, independent approach.
The high-performance LED main beam makes it possible to operate semiconductors with much higher currents than was possible just a few years ago. The new high-performance LED used by Volkswagen provides a higher luminance than normal LEDs and therefore comes very close to the laser light source. However, the luminous flux of the high-performance LED is much greater – the amount of light is thus higher than for current laser light. Noticeably positive effects for the driver include a longer range and a broader scope for headlight illumination.
Technical prototype developed in-house
The prototypes of the high-performance LED headlights installed in a Tiguan already exhibit a high degree of readiness for series-production. The design of the headlights has not yet been implemented, so purely engineering components are used. The light development (CAL Computer Aided Lighting), CAD design, thermal protection and production of the new headlights were realised by Volkswagen itself without a supplier.
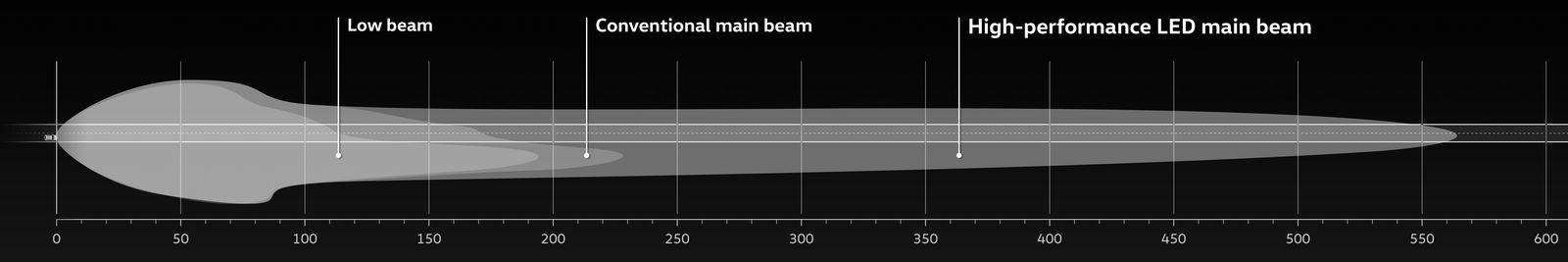
The system essentially consists of a main lens and an additional main beam. The main lens is located outside in the headlight and has a particularly flat design compared to today's systems. The aim here was to demonstrate the advantages of the new LED in terms of technical space reduction. This projection module offers a wide dipped beam, which also assumes the function of a dynamic cornering light using a swivelling support. The first main beam stage is also generated from this lens. The high-performance LED additional main beam is inside, next to the main lens. Importantly, despite the triple design of the additional main beam in the prototype only one of the integrated lenses is required. In fact the test vehicle is to be used to assess three different auxiliary headlights with individual light distribution. Tests conducted by Volkswagen have shown that almost all drivers have very individual requirements with regard to the range and width of the light beam for the main beam. The three auxiliary headlights can each be activated separately in the Tiguan. No. 1 produces a conventional additional main beam with a relatively large width. No. 2 produces a relatively small spot with a large range, while at the same time other lenses in the system illuminate the close surroundings on the right and left as well as upwards, creating a feeling of more light and thus an increase in safety. No. 3 is a concentrated spot with a range of more than 550 metres. Night driving tests should then determine which of the three auxiliary main beams is the most favoured and used in series production.